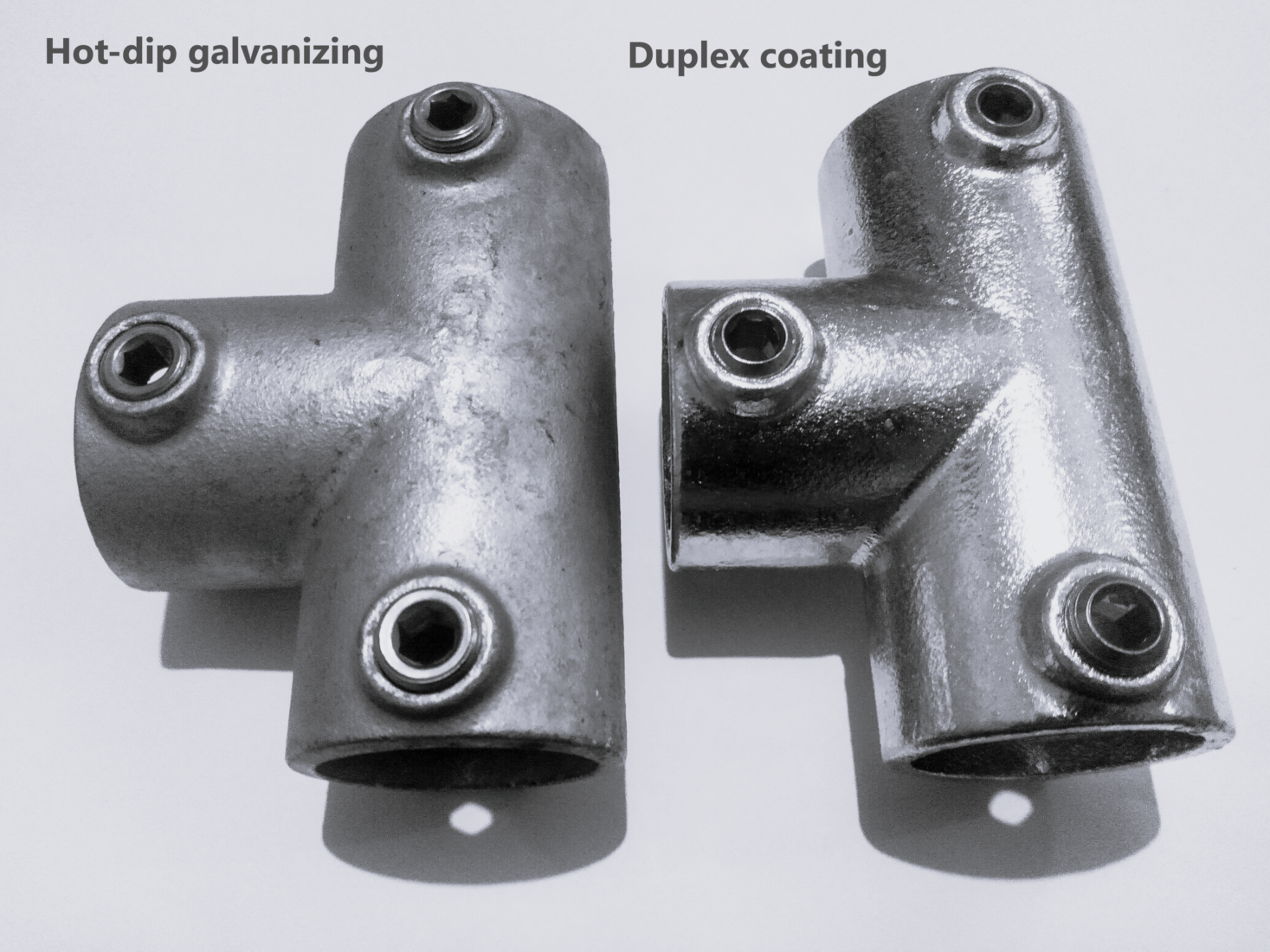
Corrosion protection
Hot-dip galvanizing (HDG) only versus duplex coating (HDG followed by electro-zinc)
DG) only versus duplex coating (HDG followed by electro-zinc) for cast iron, several factors come into play, including coating thickness, price, and the specific requirements of the application. Here’s a comparison:
Hot-Dip Galvanizing (HDG) of Cast Iron:
- Process of Hot-Dip Galvanizing (HDG) for Cast Iron:
- Surface Preparation: The cast iron components undergo thorough cleaning to remove any contaminants, such as dirt, grease, or rust, that could interfere with the galvanizing process.
- Pre-Treatment: After cleaning, the cast iron pieces may undergo pre-treatment processes such as pickling or acid washing to further clean and prepare the surface for galvanizing.
- Galvanizing: The prepared cast iron components are then immersed in a bath of molten zinc at temperatures typically around 450°C (850°F). The high temperature allows the zinc to metallurgically bond with the surface of the cast iron, forming a series of zinc-iron alloy layers.
- Quenching: After immersion, the components are removed from the zinc bath and allowed to cool in a quenching tank or by exposure to ambient air.
- Finishing: Once cooled, the galvanized cast iron pieces may undergo additional processes such as inspection, surface treatment (if required), and packaging for shipment.
- Price: The cost of hot-dip galvanizing cast iron components is influenced by factors such as size, complexity, and volume. HDG is generally more cost-effective compared to duplex coating since it involves a single coating process.
Duplex Coating (HDG followed by Electro-Zinc) of Cast Iron:
Process of Duplex Coating (HDG followed by Electro-Zinc)for Cast Iron:
- Surface Preparation:Just like in hot-dip galvanizing, the cast iron components undergo thorough cleaning to remove any contaminants such as dirt, grease, or rust. Surface preparation is crucial for ensuring proper adhesion of the coatings.
- Hot-Dip Galvanizing (HDG): The cleaned cast iron components are immersed in a bath of molten zinc at temperatures typically around 450°C (850°F). This process allows the zinc to metallurgically bond with the surface of the cast iron, forming a durable zinc-iron alloy coating. The components are then removed from the zinc bath and allowed to cool. The hot-dip galvanizing process provides a thick, durable base layer of zinc coating, offering excellent corrosion protection.
- Electro-Zinc Coating: After hot-dip galvanizing, the cast iron components undergo electroplating to apply an additional layer of zinc coating. Electro-zinc coating involves immersing the components in a zinc electrolyte solution and applying an electric current to deposit zinc onto the surface. Electro-zinc coating typically results in a thinner layer of zinc compared to hot-dip galvanizing but offers additional corrosion protection and improved aesthetics. The thickness of the electro-zinc coating can be controlled to achieve the desired level of protection and appearance.
- Finishing: Once the electro-zinc coating is applied, the cast iron components may undergo additional processes such as rinsing, drying, inspection, and surface treatment (if required). The finished components are then ready for use or further assembly into products.
- Price: Duplex coating involves additional steps and materials compared to HDG-only processes, resulting in higher production costs. The price of duplex coating for cast iron components will depend on factors such as the size of the part, the complexity of the geometry, and the desired coating thickness.
Considerations:
Corrosion Protection: Both HDG-only and duplex coatings provide corrosion protection for cast iron components. Duplex coating may offer enhanced corrosion resistance, especially in aggressive environments, due to the combined protection of the two coatings.
Aesthetics: Duplex coatings may offer improved aesthetics compared to HDG-only processes, as electro-zinc coatings typically have a smoother and shinier appearance. This may be a consideration for applications where appearance is important.
Budget: While duplex coating may offer enhanced corrosion protection and aesthetics, it comes at a higher cost compared to HDG-only processes. It’s essential to weigh the benefits against the additional expense to determine the most cost-effective solution for your application.







